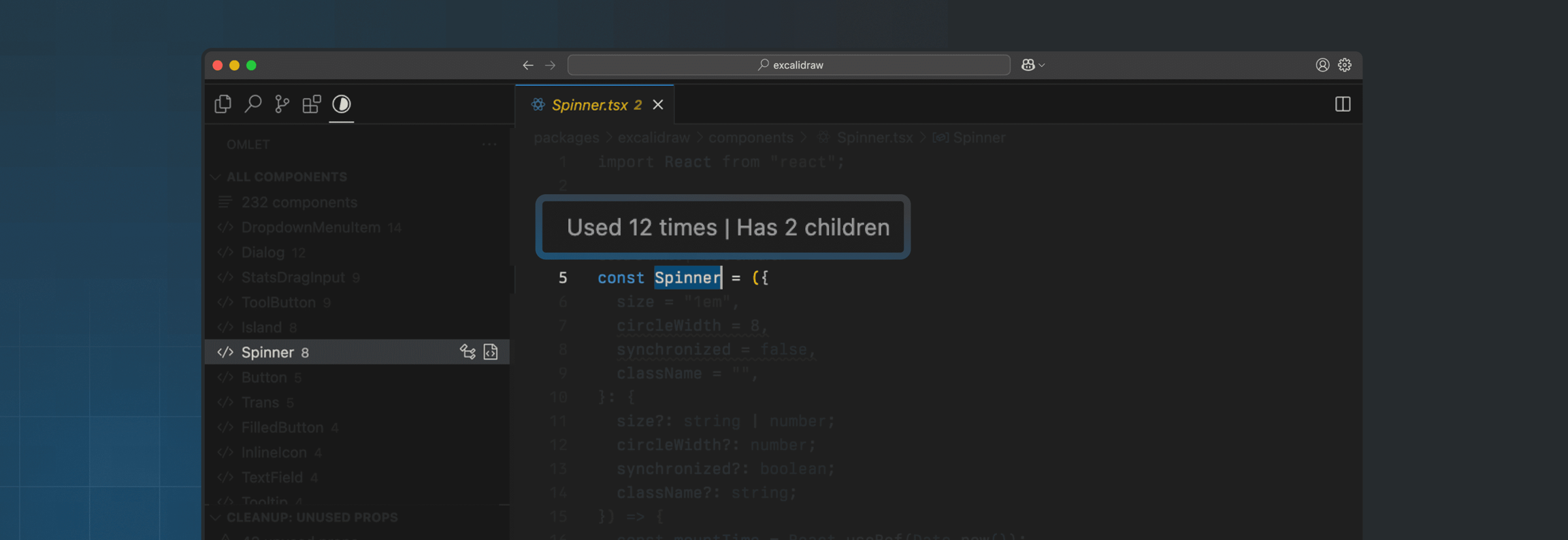
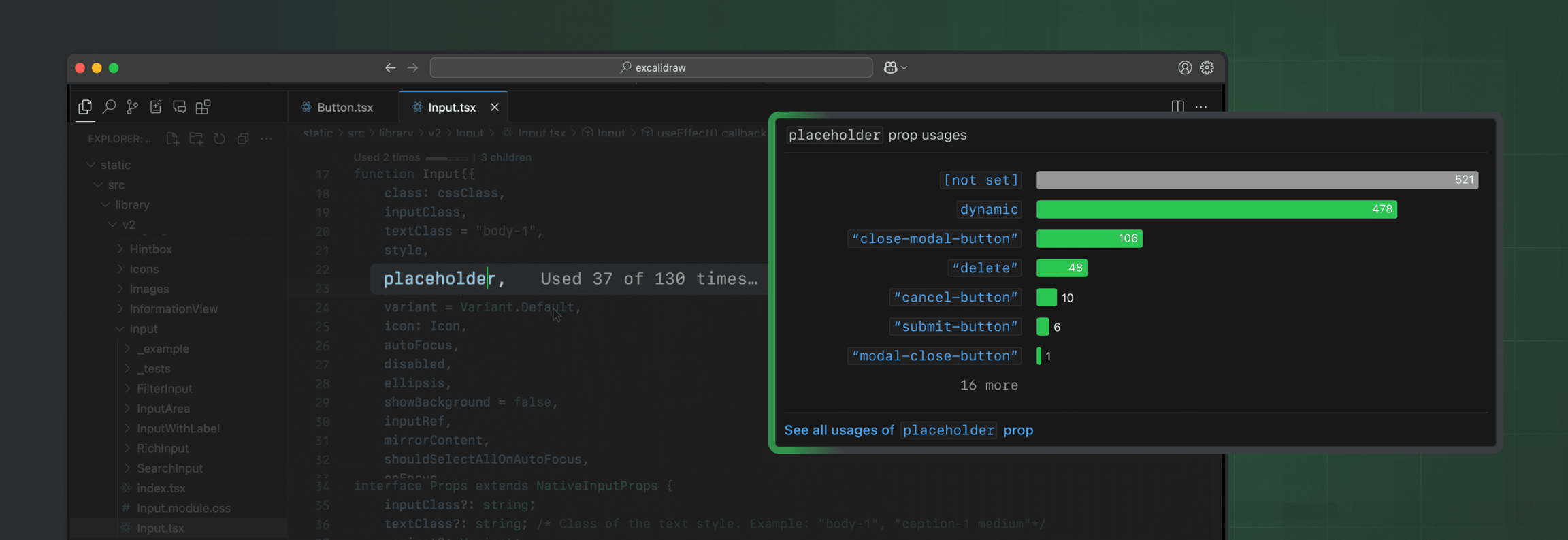
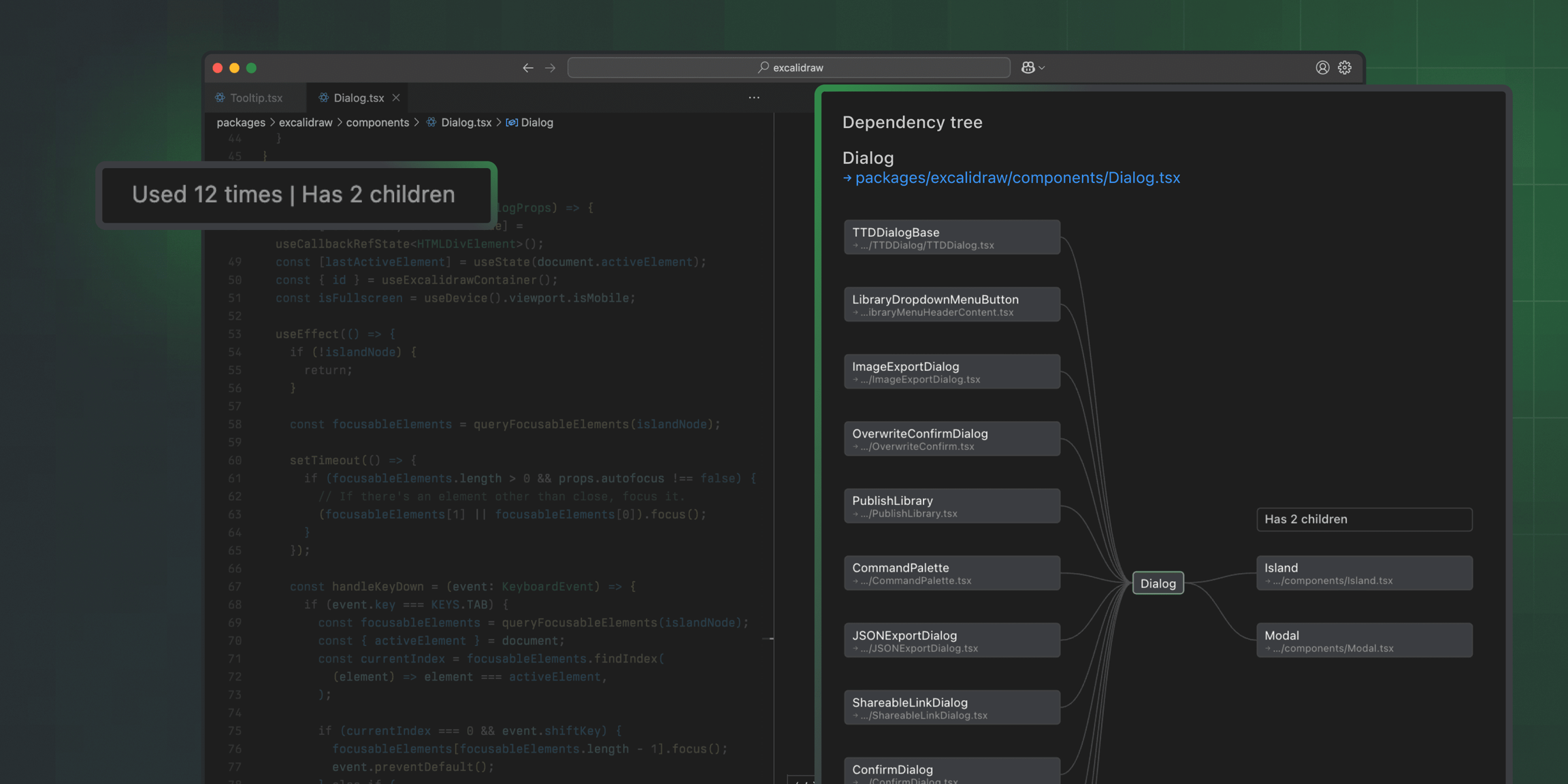
Omlet for VS Code
Guide to help you get started with Omlet's VS Code extension.
Quick demo
Installation
Get started
No React components found?
Having performance issues?

Need more data?
What's next?
Last updated